Choosing the Right Threadlocker
When vehicle repair instructions call for threadlocker use, knowing the difference between each type and color designation will save you a lot of trouble.
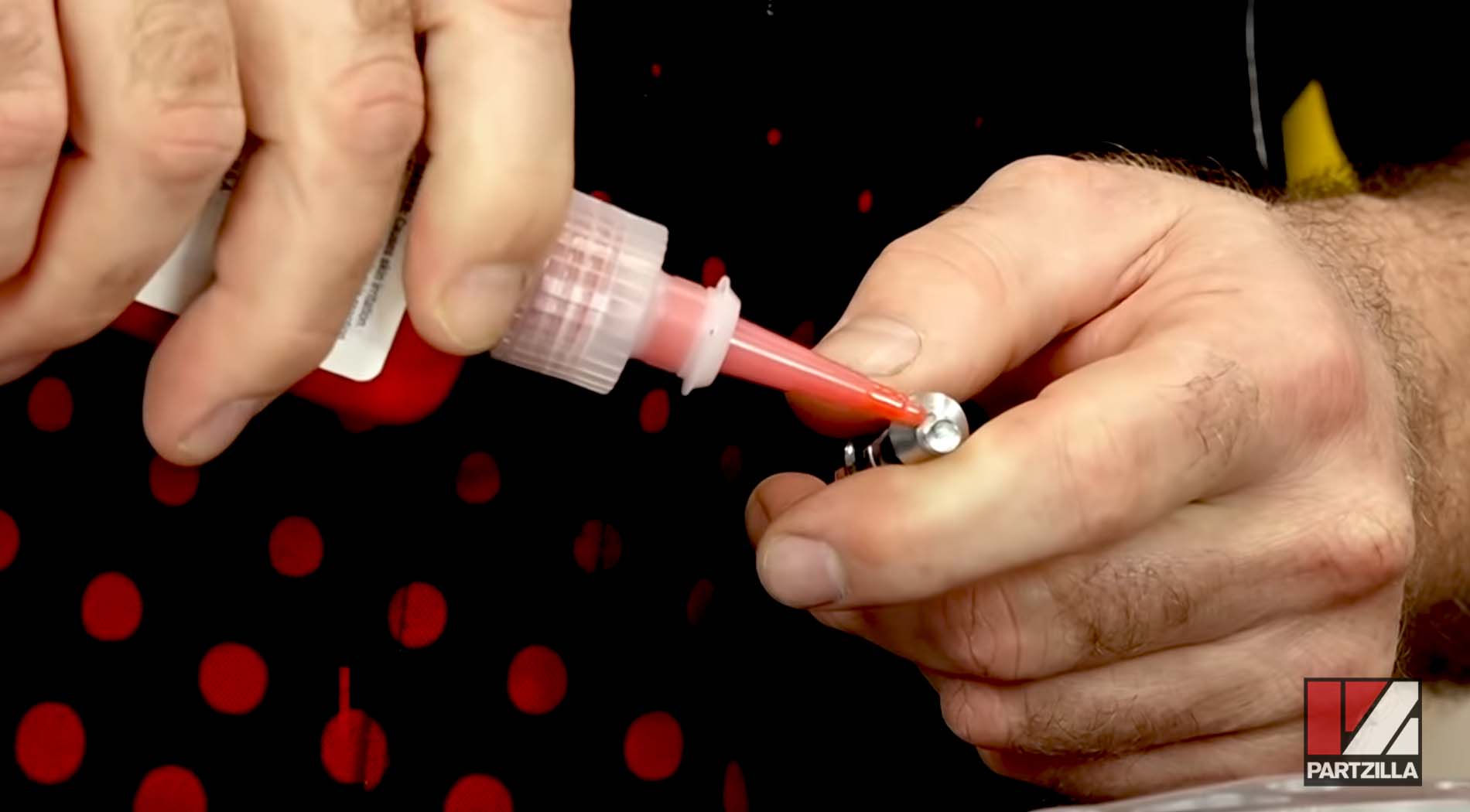
What is Threadlocker?
Threadlocker is a liquid that seals and locks threaded metal fasteners. When applied to the threads of a fastener, the liquid threadlocker flows into the gaps between the threads and fills them.
Without any oxygen, the threadlocker cures and hardens, and in doing so generates a seal, locking the threads together so the fasteners won’t come loose even when shaken. This is why threadlocker is essential in the assembly of engines or suspension systems that constantly experience movement and vibration.
Threadlocker Color-Coding
Red Threadlocker
The highest strength threadlocker, with a shear strength of up to 225 foot-pounds of torque before the threadlocker’s hold is broken. Red threadlocker can be used on fasteners up to 1 inch in diameter, and can withstand temperatures of up to 300°F. It’s commonly used on internal engine fasteners, vehicle suspension fasteners, and wheel studs. Fasteners with red threadlocker require extreme heat (over 450°F) before they can be disassembled.
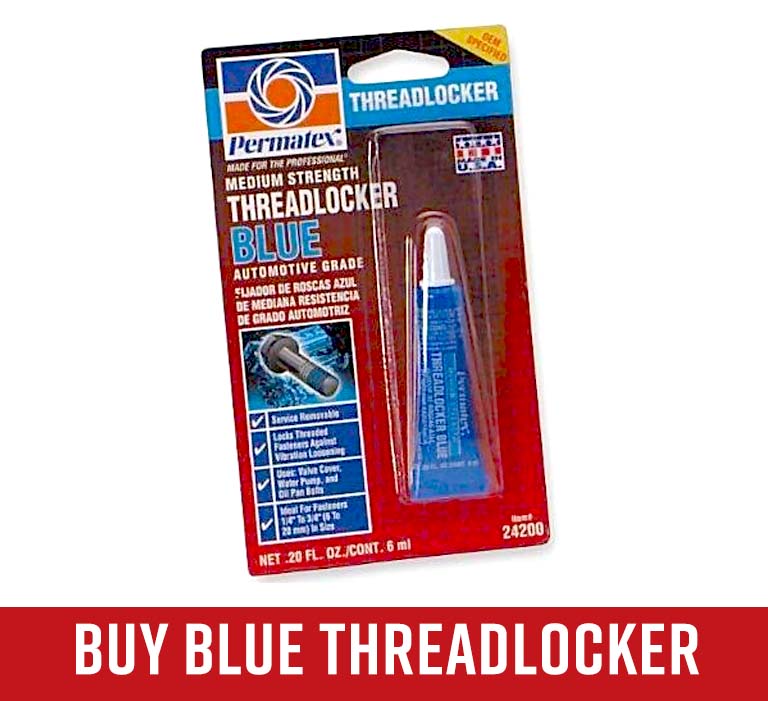
Blue Threadlocker
The medium strength threadlocker, with a shear strength of up to 150 foot-pounds of torque before the threadlocker’s hold is broken. Blue threadlocker can be used on fasteners up to ¾ inch in diameter, and withstands temperatures up to 300°F. It’s commonly used on valve covers, oil pans, and water pumps. Fasteners with blue threadlocker can be disassembled with regular hand tools.

Purple Threadlocker
The lowest strength threadlocker, with a shear strength of up to 120 foot-pounds of torque before the threadlocker’s hold is broken. Purple threadlocker can be used on fasteners up to ¼ inch in diameter, and withstands temperatures of up to 300°F. It’s commonly used on low-strength metals such as aluminum or brass, and fasteners with small thread sizes to avoid shearing during disassembly. Fasteners with purple threadlocker can be disassembled with regular hand tools.
Green Threadlocker
The wicking threadlocker, which can penetrate into the threads of engaged fasteners, so there’s no need to disassemble them for the threadlocker to be applied. Green threadlocker is of medium strength and commonly used on electrical connectors and instrumentation fasteners.
These descriptions are generalizations of each color-coding of threadlocker, since products exist of the same color designation with slightly varying properties. For example, the Loctite brand blue threadlocker 243 is resistant to oils, whereas the Loctite blue threadlocker 242 is not. Also, the exact strength of a particular threadlocker product varies by manufacturer (Loctite, Permatex, etc.).
How to Choose the Right Threadlocker
When choosing the correct threadlocker for a particular application, you’ll need to consider the strength the threadlocker will be required to provide; the size of the fasteners; the heat the threadlocker must withstand; whether the threadlocker will be exposed to chemicals; and whether the fasteners will need to be disassembled again.
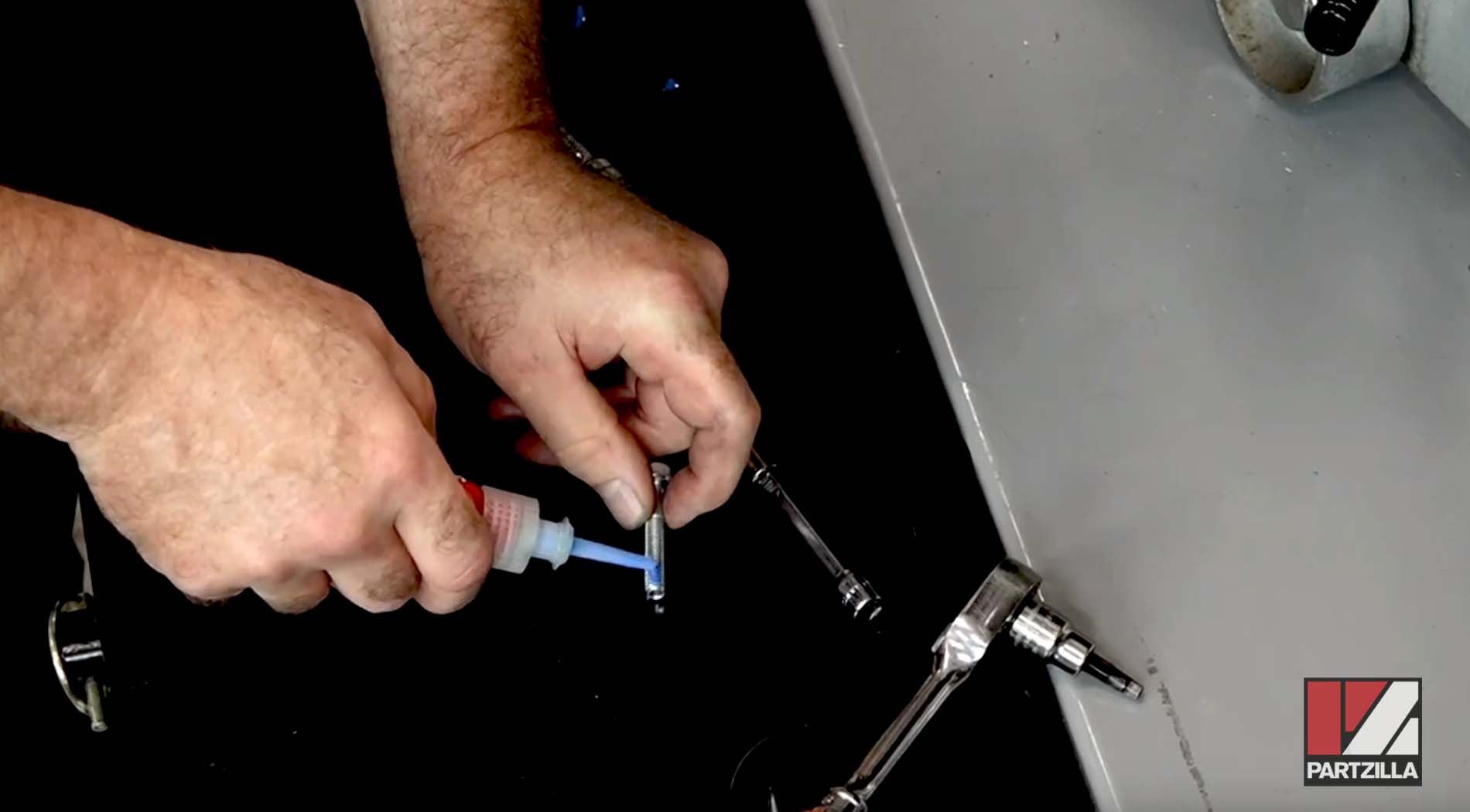

Strength and Size
If the fasteners will be tightened to a high torque, the threadlocker’s shear strength needs to be strong to prevent the torque breaking its hold on the fasteners, and to keep its hold if it’ll encounter repeated vibrations. Stronger threadlockers are better suited for larger diameter threads, while low-strength threadlockers are better for smaller diameter threads, where shearing may be a risk with a stronger threadlocker.
Chemicals and Heat
The threadlocker must be able to withstand the heat the fasteners operate in without losing its hold, and be resistant to and unaffected by any chemicals it may come into contact with, such as oils or fuels.
Using Threadlocker
Most service and repair jobs require blue or purple threadlocker. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions in a service manual or included with an OEM part if you’re not sure.
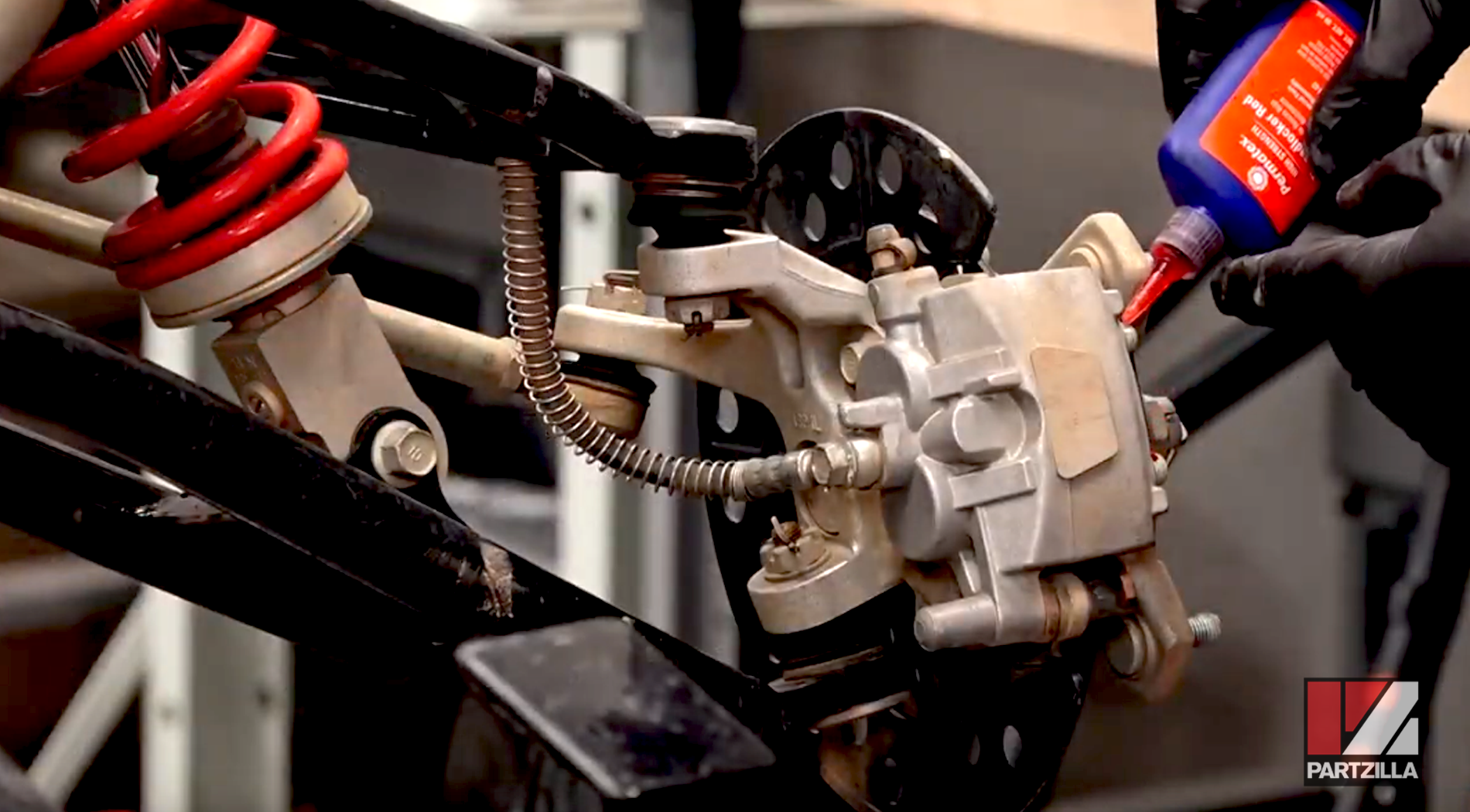
When applying threadlocker, use just enough to coat the threads where the fasteners meet. Any more than that is a waste of product and money. Use a single drop of threadlocker on smaller threads, and 2-3 drops on larger threads.
Threadlocker is a chemical compound with a limited lifespan that becomes less effective over time. Each threadlocker product lasts about a year from when you first opened it, so expect to replace it every 12 months whether you used it up or not.









